IHS Advanced Studies Summer Seminar, “Liberty & Scholarship: Challenges and Critiques” Bryn Mawr College, Philadelphia, PA.
Date: 13-19 June, 2015
Lectures on:
- “The Classical Liberal Tradition – A History of Ideas and Movements over 400 Years” – two lectures
- “Images of Liberty and Power: State Propaganda and its Subversion”
- “Competing Visions of the Future: Socialist and Classical Liberal”
Lecture 1. “The Classical Liberal Tradition: Theory and History (A Two-Part Lecture)”
Lecture material:
Outline:
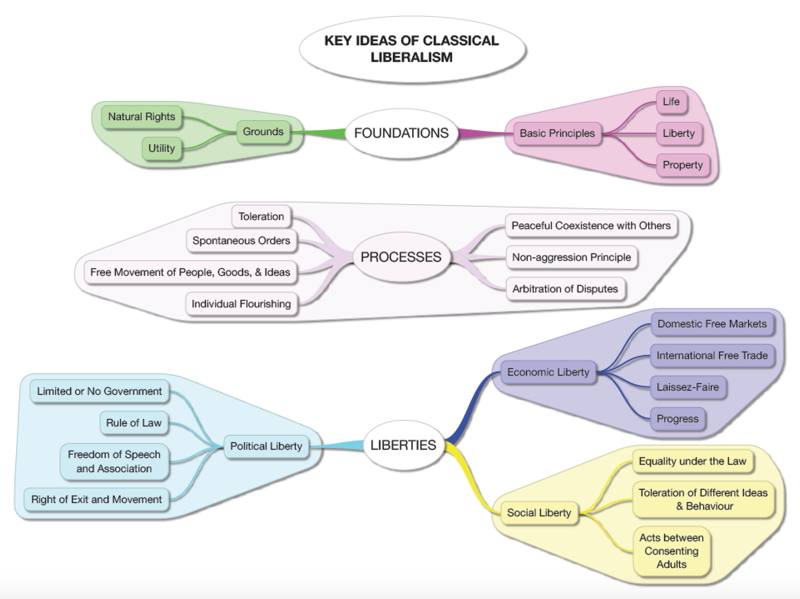
There are some inter-related threads I wish to explore on the Classical Liberal Tradition (CLT):
- an examination of the tradition of political and economic thought which came to be known as “classical liberalism” (in the 19th and early 20th centuries) or “libertarianism” (in the second half of the 20th century);
- what these Classical Liberals believed in (my Concept Map of CL and “12 Key Concepts”) and
- what they opposed
- a brief survey of the history of the Classical Liberal Tradition (CLT) over the past 400 years (1640-2015), with an emphasis on 4 particular historical periods:
- 1640s: the English Civil War/Revolution
- 1750-1790: the American and French Revolutions
- the long liberal 19th century 1815-1914
- the post-WW2 liberal renaissance
- why was there a greater flourishing of CL then?
- emergence of new ideas about liberty?
- greater willingness to act on these ideas in order to change society
- reaction to increases in State Power or crises in the State (war and debt)?
- these reactions were of two different kind:
- “conservative” CL: resisting state imposed changes on traditional religious, social, political, economic practices
- “revolutionary” CL: seeing the possibilities of bringing freedom to those who have never enjoyed it before, women, slaves, serfs, women; or moving society into new, radical pro-freedom direction which has never existed before (free trade, laissez-faire, privatising public goods)
- a discussion of the theory and history of the spread of Classical Liberal ideas and what this means for developing a better strategy for the future (Discussion Group)
- ideas and interests (Mises)
- the production, dissemination and consumption of ideas: the role of producers, investors, entrepreneurs, salespeople, and consumers of ideas
- the nature and speed of ideological change