[Note: This post is part of a series on the History of the Classical Liberal Tradition]
This idea map is designed to give you an overview of what I think are the essential features of the classical liberal tradition as it has evolved over the past 400 years.
See my Study Guides on the Classical Liberal Tradition for more details.
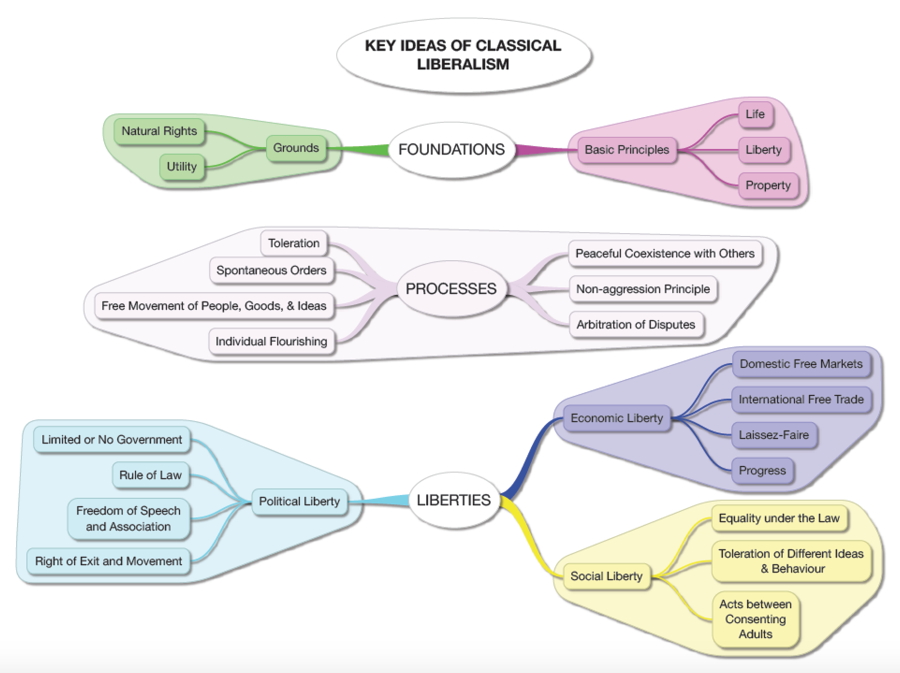
The Grounds of CL Ideas
The Basic Principles
The foundations for these beliefs are based upon the following:
- the basic principles
- life
- liberty
- property
- the philosophical grounds for belief
- natural law (God’s Law) and natural rights
- utility
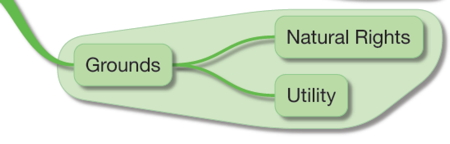
The Processes for Achieving and Sustaining a Free Society
The processes by which these principles are carried out/put into practice; how people interact with each other
- the non-aggression principle
- voluntary cooperation
- toleration
- free movement of people, goods, & ideas
- individual flourishing
- peaceful coexistence with others
- arbitration of disputes
- spontaneous orders
Liberty as “the sum of all freedoms”
Liberty should be seen as a “bundle” or “cluster” of freedoms which together make up what is “Liberty”. Bastiat stated it in this way:
And what is liberty, this word that has the power of making all hearts beat faster and causing agitation around the world, if it is not the sum of all freedoms: freedom of conscience, teaching, and association; freedom of the press; freedom to travel, work, and trade; in other words, the free exercise of all inoffensive faculties by all men and, in still other terms, the destruction of all despotic regimes, even legal despotism, and the reduction of the law to its sole rational attribution, which is to regulate the individual law of legitimate defense or to punish injustice.
Source: Frédéric Bastiat on LIBERTY as the sum of all freedoms (1850) – quote from The Law (June 1850)
LIBERTY is compromised of three main bundles of freedoms:
- political/legal freedoms
- limited (no) government
- the rule of law
- freedom speech and association (religion)
- right of exit/entry (movement or new govt)
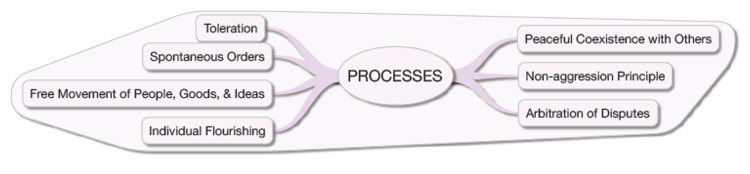
- economic freedoms:
- domestic free markets
- international free trade
- laissez-faire
- progress
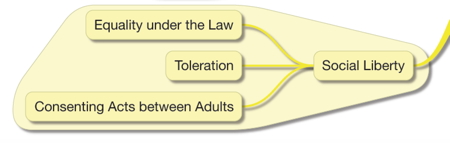
- social freedoms
- equality under the law
- toleration of different ideas and behaviour
- acts between consenting adults